“The heartfelt testimony given by members of our community in the course of the summer has made it searingly clear that racism is also present here at Fordham,” Father McShane said in his September 12 State of the University address, referring to stories of discrimination students and alumni of color shared, largely on social media.
“As painful as that admission may be, we must face up to it. Therefore, let me be clear: anti-racism, diversity, and inclusion are institutional and mission priorities at Fordham.”
Case in point: The trustees have mandated annual anti-racism training for all faculty, students, staff, and administrators—including the president’s cabinet and the board itself. And they have charged the newly renamed Mission and Social Justice Committee with ensuring that diversity and anti-racism are central to the University’s efforts.
In late October, Fordham Magazine brought together six members of the board for a candid discussion of bias, inclusion, and what it will take to bring about meaningful, lasting change at the University and beyond.
The Participants
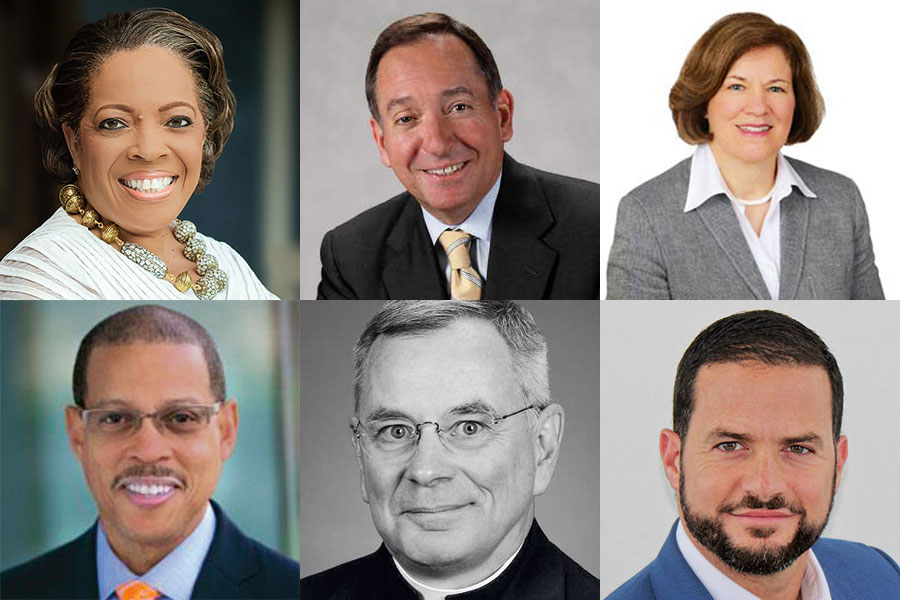

VALERIE RAINFORD, FCRH ’86
Moderator
Valerie Rainford is the CEO of Elloree Talent Strategies. Previously, she was a managing director at JPMorgan Chase, where she led the company’s Advancing Black Leaders strategy. She also had a 21-year career at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, where she was the first Black woman to rise to senior vice president. She is the author of Until the Brighter Tomorrow: One Woman’s Courageous Climb from the Projects to the Podium (Elloree Press, 2014). A Fordham trustee since 2019, she is currently spearheading anti-racism trainings among the trustees and within the University as part of Fordham’s action plan for addressing racism.
ROBERT D. DALEO, GABELLI ’72
Chair, Fordham University Board of Trustees
Bob Daleo is a former vice chairman of Thomson Reuters, where he served as executive vice president and chief financial officer before retiring in 2012. He joined the Fordham Board of Trustees in 2008 and was elected chair in 2012.
MARY ANNE SULLIVAN, TMC ’73
Vice Chair, Fordham University Board of Trustees
Mary Anne Sullivan is senior counsel at Hogan Lovells. Previously, she served as general counsel for the U.S. Department of Energy. She became a Fordham trustee in 2016 and has been vice chair of the board since 2018.
ANTHONY P. CARTER, FCRH ’76
Anthony Carter retired in 2015 as vice president and chief diversity officer at Johnson & Johnson. At Fordham, he has served as a member of the Diversity Task Force, and in 2017 he led the search committee for a chief diversity officer. He joined the board in 2018 and is now co-chair of its Mission and Social Justice Committee.
THOMAS J. REGAN, S.J., GSAS ’82, ’84
Father Regan was named superior of the Jesuit community at Fordham in July 2020. He previously served as dean of the College of Arts and Sciences and the Graduate School at Loyola University Chicago, and as a Fordham trustee. He rejoined the board this year and is now co-chair of its Mission and Social Justice Committee.
GUALBERTO RODRIGUEZ, FCRH ’95
Gualberto Rodriguez has been the chairman of Grupo Navis since 2017 and managing partner of Semillero Ventures since 2016. From 2005 to 2017, he served as president of Grupo Navis, the San Juan, Puerto Rico-based firm that was founded by his grandfather in 1960 as Caribbean Produce Exchange. He joined the Fordham Board of Trustees in 2019.
The Discussion
This conversation has been edited and condensed for clarity and space.
VALERIE RAINFORD: So, the world has this problem, and many feel it’s pretty overwhelming and don’t know where to start. What gives you hope that we can make progress at Fordham?
BOB DALEO: One of the intentional actions we are taking is refining the focus of the trustees’ Mission and Social Justice Committee, which has oversight responsibility for our antiracism strategy. If we’re going to cure this, you have to start at the board level to make sure that the institution has in its process what the Jesuits have in their heart. And that’s a hard transition, to go from head and heart to how we behave as an institution.
We are an organization whose mission has always been about social justice. We’ve always talked about educating young men and women for others. What does that mean if it’s not for all others?
Calling out “social justice” in the title of this committee is our way of deliberately emphasizing our intent and ensuring that we stay focused.
We don’t have all the answers, but we are committed to combating racism, overt and covert, and doing our part to ensure the opportunity and ability for all to generate real wealth, to share in the American dream.
Understanding the Pain
In conversation, the trustees discussed some pernicious examples of bias and racism that students have experienced on campus in recent years—and they related those instances to their own experiences as undergraduates. Allowing these intensely personal stories to surface, they said, is part of the process of spurring the entire Fordham community to reflection and action.
RAINFORD: Are there specific experiences with racism that drive how you think about the work we are undertaking?
ANTHONY CARTER: We had an issue on campus several years ago when I was on the President’s Council. It was explained to me that a Black student, on move-in day—one of the most enthusiastic days for students—went downstairs to bring more stuff up to his dorm room, and when he got back, the N-word was carved into his door.
I wasn’t a trustee at the time, but my son had just graduated a year or so before that happened. I didn’t ask what is wrong with the school. I asked, what’s wrong with our students and families? Our focus was on making sure that the student did not feel the incident was systemic; it was not the baseline of what happens at Fordham.
That example brought back memories that I had of the white student union as a Fordham undergraduate during the 1970s, and my feeling, as a grown man still experiencing these things, is, how do we console? How do we make someone feel whole again? How do we make folks who are constantly subjected to this feel that we are better than this, and that your very being here, and that very experience here, indicates we have a lot of work to do?
I am emboldened, I am hopeful, because the leaders on this team believe as I do, that there’s zero tolerance for racism at Fordham University. And I think our students need to know that.
MARY ANNE SULLIVAN: Hearing Anthony’s examples makes me think of the Instagram posts by Fordham students and alumni after George Floyd was killed, and how shocked and hurt I was at how some Black students had been made to feel unwelcome. There was a story of a student who brought his little brother to see Fordham, and while he was giving his little brother a tour of the campus, he got challenged that he “didn’t belong” there. Having brought my little sister to campus when I was an undergraduate, and having her be so welcomed—it just crushed me to see that Black students were having such a different experience.
RAINFORD: Mary Anne, were you surprised, or was it the contrast that made you feel crushed?
SULLIVAN: It was the contrast, that I had done something so similar and had such an absolutely opposite experience.
GUALBERTO RODRIGUEZ: What it brought up for me is an experience I had in the first month of sophomore year at Fordham. I was in a U.S. history class, and the professor called on me to finish a very common American nursery rhyme parents use to put their kids to sleep. I didn’t know it, and he put me on the spot in front of the entire class by asking, “How come?” “Well, I’m from Puerto Rico,” I responded. And he’s like, “Isn’t that part of the U.S.?”
I felt so ashamed, that I really didn’t belong. I ran to my new theology professor, a Jesuit, and, like Anthony said, he consoled me. He made me realize, “You do belong. I know this professor. He’s a very kind man. He just doesn’t know about your background.”
I had written a letter, in my fear that I somehow found myself in the wrong place. He read my letter—I was trembling—and he said, “I think you should send this to him, and you should have a conversation.” So, my Jesuit professor, through the wisdom of his loving advice, empowered me to take on this issue by myself. And it was a beautiful conversation with a very kind man who simply had never thought about why a student from Puerto Rico would not know a common nursery rhyme in the States.
So my hopes are, in this whole process of tackling racism, that we dig deep for the Jesuit approach, a very loving, consoling, compassionate one, focused on justice with compassion, without anger.
THOMAS REGAN, S.J.: I taught for 19 years at Fairfield University in Connecticut. And Connecticut prides itself on planting dogwood trees. Every spring they have this magnificent dogwood festival, and the colors are just breathtaking. I was living in a residence hall, and I said to the student who lived next door to me, “I know it’s finals, but you need a little break from studying. You have a car. Go up to Greenfield Hill, and just allow yourself to see the beauty of Fairfield.” And so after dinner that night, I walked by his room. I said, “How was the dogwood festival?”
And he says, “Well, it was really pretty, but I got stopped three times by the police in Fairfield.” And your heart just goes out to him. Why can’t he go up to Greenfield Hill, like any other student, and have an enjoyable experience? Why is he deprived of that?
RAINFORD: So, the unfortunate reality is that racism is not new and is as prevalent today as ever. Each of us has seen it before, but have we taken it on to end it? To make it clear that as an organization, we will not tolerate racism? Now is the time to openly and proactively take it on as trustees of this great institution that we all love.
Making Anti-Racism Part of the Fordham DNA
The trustees spoke about the need to root out racism at the University in a systemic way, and why, despite a host of challenges related to remote learning and the ongoing economic and social impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, they are committed to using the board’s authority to unite the community in combating racism and educating for justice.
RAINFORD: What are your thoughts for how we will embed anti-racism policies and practices in how we lead as a board?
CARTER: What I want us to be conscious of is that while we don’t have all the answers, the questions that we’re asking as a governance body can lead us to look for solutions. And not only look for solutions but to hold leaders in the Fordham community and beyond accountable for those solutions.
But there are two things, I call them syndromes. One is the fatigue syndrome. And one is the obvious racism syndrome. The fatigue syndrome allows us to believe, “Oh man, this has been going on for so long.” And I hear this from a lot of my white friends. “It’s not the time to talk about this. Since George Floyd and all the things happening before that, we’re just so fatigued.”
The racism syndrome says to me that we at Fordham have all made ourselves accountable. Whether we experienced racism or not, with our action plans, we embrace the fact that racism affects us all. This is not the time to be fatigued.
There are some things embedded in our strategic plan around this topic. But now we have embraced anti-racism policies and behaviors and mechanisms to solve this thing in a way in which we own it. And our Fordham community must know that, because we put people on notice. We put our own board on notice.
SULLIVAN: If we’re going to be relevant going forward, we have to make rooting out racism part of our DNA. This can’t just be a nice-to-have that we do on the side. It has to be a systemic change that comes about by a thousand different actions we take. It has to be part of our course offerings, part of our student body, part of our faculty, part of our public safety force.
It’s got to be everybody’s job to make Fordham relevant for the future. And the reality is, the future has many more students of color who are going to be looking for places in college, and a society that demands that we be representative of the communities we live in.
At my law firm, we cannot put forward a team for a client on a project if we don’t show that we are including members of color. And Fordham’s role is to fill the pipeline so that those people are there.
And Anthony, we do have a lot in the strategic plan that was already focused towards educating for justice, diversity, equity, and inclusion, but we’re now saying with everything we look at, how is it responding to the issue of racism in our society? How are we fixing the problem at Fordham in this one area, in this one area, in this one area?
We have four broad goals in the strategic plan, and I would say three of the four pretty explicitly lend themselves to anti-racism objectives. Holistic student development—addressing the needs of students to feel respected, to feel consoled, when necessary. Walking with our community. We sit in New York City, a very diverse community, and we are not nearly as diverse as the community we sit in. The goal is to develop more partnerships of all kinds that will engage the broader community. We are looking for ways to strengthen what we’re doing to have a greater impact. For example, cybersecurity is an area where we are partnering with the historically Black colleges and universities on a cybersecurity initiative. The fourth broad objective is STEM-plus. I would say people of color are underrepresented in STEM.
I’m a to-do list kind of person, and so I want to see what’s on our to-do list that is going to address this problem so we’re not just having pious thoughts and writing beautiful statements.
Changing the Way Fordham Looks
The trustees spoke about the barriers between Fordham’s campuses and the surrounding areas of New York City, and of efforts to recruit and retain diverse faculty and students.
RAINFORD: Maybe this is for you to help us with, Father, but what is Fordham’s unique opportunity given its Jesuit traditions around social justice? And what’s the thing that gives us the ability to do this differently than probably any other university in New York City?
FATHER REGAN: We have to change the way that Fordham looks. I’m just coming off six years of being dean of arts and sciences at Loyola University Chicago, and every time we hired a tenure-track faculty member, they sent three candidates up to the dean. And so I said, “If we don’t have a person of color on that list, you’re going to get it back.” It’s very competitive, but you have to be really intentional that you’re going to do this and hold people to the fire. Whoever is applying, the HR managers have to say, “Bring me a diverse slate of candidates and let’s change the way that Fordham looks.”
To speak to the Jesuits, we have this incredible Jesuit network. We could create scholarships for the students coming out of the 56 Jesuit high schools in the U.S. If you’re a person of color, you have a home at Fordham. We’re in New York; you can’t get a more diverse city than New York. And so we have to be reflective of this city.
But we also have to make people feel welcome. Because I listen, and see on Instagram—the students want to come, people who work here want to come, but they want to see people who look like them. We really have to say, this is who we are and we’re going to put up the money to make this happen.
RODRIGUEZ: It strikes me that there would be a special Fordham Jesuit way to address, on a day-today basis, the issues of inclusion and racism. That is what I would like to draw from the Jesuit tradition, this idea of comforting and consoling and reconciliation. That could make the process of having a different look to the faces—the process itself—interesting.
For example, an invitation to a prospective African American faculty or staff member would be to be part of a process of change. We have a Jesuit way to explore that experience of not yet being the end result. I think that will make us a very interesting lab as an institution for people who like to be the astronauts, the first on the moon, to experience that in a safe, consoling, socially interesting laboratory.
RAINFORD: I love that concept of a lab for anti-racism, done in a Fordham way, rooted in the Jesuit tradition. Now, how do we get that done?
Mastering the Architecture of Reform
Since the spring, deans, faculty, administrators, students, and staff have been working to advance Fordham’s anti-racism goals, but in conversation, the trustees expressed the need to establish a framework to ensure that the community’s efforts are not only unified but sustainable.
DALEO: In establishing a framework, the first thing you want to do is set the strategy; then you say, as an organization, “Okay, do we have the structure to properly implement that strategy?” And then the third thing is, “Do we have the people in that structure to run that process to implement the strategy?” I think one of the most important things we can do as a board is to be nudging the organization on these issues.
As a board, the one thing I’d like us to always come back to is, “Okay, these are great ideas. How do we get it done?”
We must also continually remind ourselves that our role is one of oversight. We are not the strategists but instead evaluators of the strategy. We have tremendous power, if you will, by shaping that, by pushing back and saying, “Nope, that isn’t quite right. Go back and think about it again.”
CARTER: This is moving. It’s motivating. We can be the masters of the architecture around designing inclusive behavior.
For example, we invite faculty to our board meetings, typically department heads; we should invite faculty of color to periodically meet with us. As the governing body, we determine how we want to engage. And from that engagement, we can become more solutions-oriented. “We’re here to hear you. What can we do?”
FATHER REGAN: Higher education has changed so dramatically, and the pandemic has just put that in floodlights. What does a university do? How is it going to look different after the pandemic? That’s exciting. That’s exactly where we need to go.
CARTER: I’m encouraged by the reports we get on what’s going on with COVID-19, how the University is proactively managing the crisis to protect the Fordham community. It is data-laden, well-researched; there is direction to it. Now we need to say, with that same sort of vigor, how do we apply that to those things that focus on social justice? How do we make that an agenda item with data, with information to measure our progress?
Once you tell somebody, “I need a report on that,” people get pretty serious. So, I think we have the energy to keep us aware of what’s going on with this backdrop we’re living in, but what are the other components that might be missing from those presentations that we need to know?
SULLIVAN: When we’re meeting in person as a board, we routinely have a lunch speaker. I would suggest that we set an expectation that whoever is presenting will address anti-racism. What is their school doing? What is their part of the University doing on this subject to advance our goals?
DALEO: I love all of your ideas, including the suggestion to increase our interaction with students and faculty of color so that we can talk about and learn how these issues affect them directly. As we move forward, the key will be to continually look for ways to institutionalize improvements for long-lasting change. Let’s continue to have these kinds of open discussions more broadly, because it’s easy to get frustrated by the problem of racism, to not know how to solve it.
I believe, and I think Fordham believes, the way you change the world is one life at a time. Our actions need to ensure that we are impacting every single life.
RAINFORD: Team, the essence of this conversation is that while we don’t have all the answers, the board is proactively engaged and owning the challenge. We’re committed to pushing each other and pushing the organization and asking all the questions that will continue to move the organization forward to create sustainable and equitable change. Thank you!
Addressing Racism, Educating for Justice
The University’s anti-racism plan features six broad goals and nearly 40 concrete action steps.
Six Goals, Six Examples of Work Underway
1. Develop robust admissions strategies for effective recruitment of students of color.
Fordham is expanding pipeline programs with local schools, such as Cardinal Hayes High School in the Bronx, that have a high number of Black and Latinx students.
2. Recruit and retain a more diverse faculty, administration, and staff.
Of 26 arts and sciences full-time tenure/tenure-track faculty members hired this year, 50% are persons of color.
3. Develop curricular and cocurricular initiatives that support the imperative of confronting racism and educating for justice.
With support from Teaching Race Across the Curriculum grants, academic departments are integrating questions of race and justice into introductory courses.
4. Create a more welcoming and affirming campus.
A multicultural center will be part of the campus center expansion at Rose Hill, and a similar center will be established at Lincoln Center.
5. Build lasting partnerships with our neighbors.
Fordham has joined the Bronx Is Reading to co-sponsor and co-host the annual Bronx Book Festival and other events.
6. Amplify our voice in educating for justice beyond the campus.
The Center on Race, Law and Justice recently hosted a webinar on police reform that included Benjamin Tucker, LAW ’81, first deputy commissioner of the New York City Police Department.